Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 |
Tags
- 자바
- lv0
- 백준 N과 M 자바
- 프로그래머스 풀이
- 오름차순 정렬
- index of
- 문자열
- 백준
- 알고리즘
- 이진수 변환
- 프로그래머스 문자열 정렬
- 프로그래머스 자바
- 스프링부트 도커 배포
- 클라이언트
- 스택
- 스프링부트 도커
- Queue
- SWEA
- StringTokenizer
- Programmers
- 큐
- COS Pro
- java
- Stack
- Lv1
- 프로그래머스
- 삼각형의 완성조건
- lv2
- 버퍼
- 스프링부트 도커로 배포
Archives
- Today
- Total
mun dev
이코테 2. DFS와 BFS 알고리즘 본문
DFS(Depth First Search)
- DFS는 깊이 우선 탐색이라고도 부르며 그래프에서 깊은 부분을 우선적으로 탐색하는 알고리즘
- DFS는 스택 자료구조(혹은 재귀함수)를 이용
- 동작과정
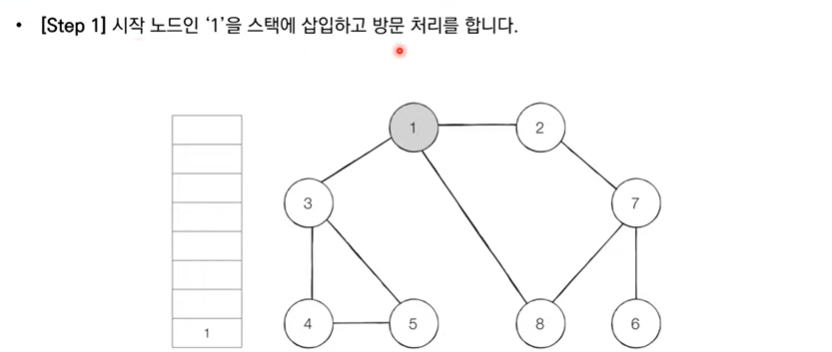
- 탐색 시작 노드를 스택에 삽입하고 방문처리
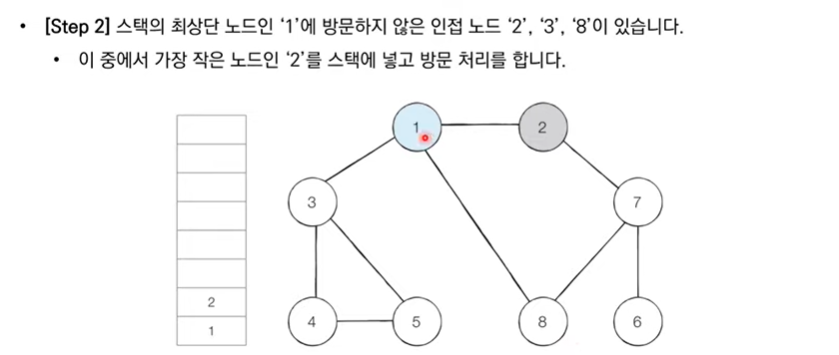
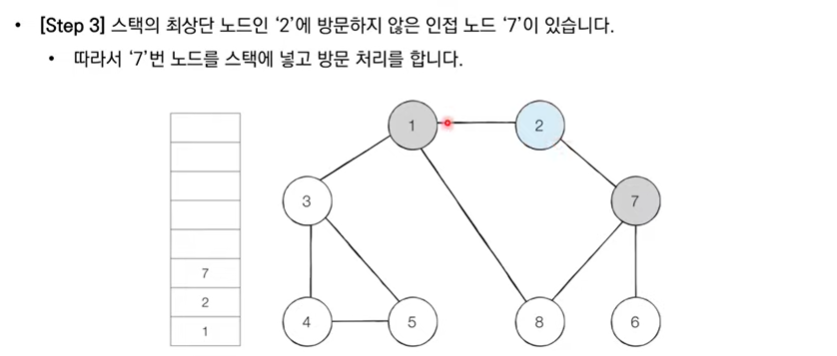
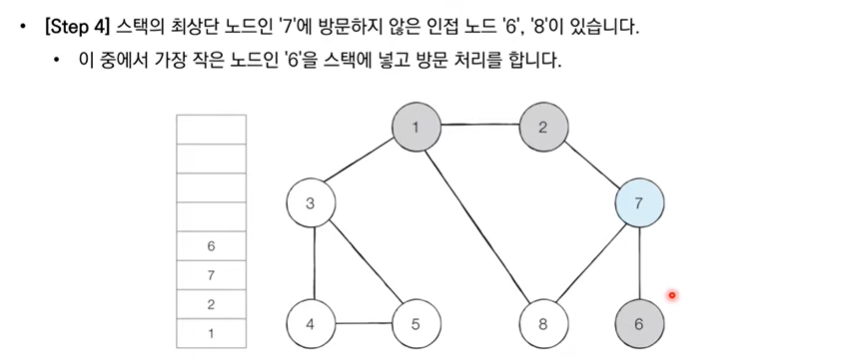
- 스택의 최상단 노드에 방문하지 않은 인접한 노드가 하나라도 있으면 그 노드를 스택에 넣고 방문 처리
- 방문하지 않은 인접 노드가 없으면 스택에서 최상단 노드를 꺼낸다.
- 더 이상 2번의 과정을 수행할 수 없을 때까지 반복
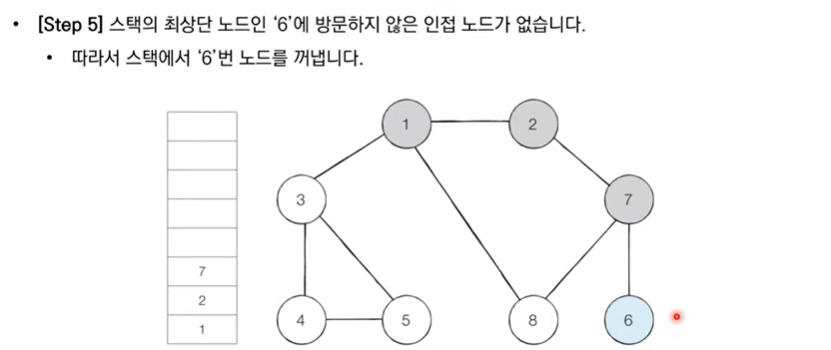

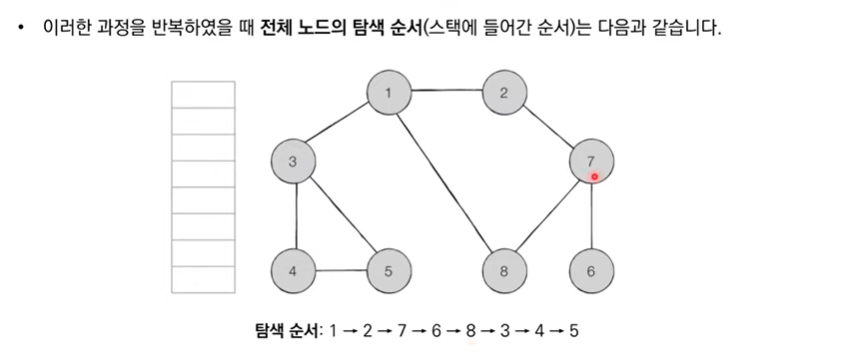
DFS 구현 예제
위 과정을 구현한 코드입니다.
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static boolean[] visited = new boolean[9];
public static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
//DFS 함수 정의
public static void dfs(int x) {
// 현재 노드를 방문 처리
visited[x]=true;
System.out.print(x+" ");
// 현재 노드와 연결된 다른 노드를 재귀적으로 방문
for(int i=0; i<graph.get(x).size(); i++){
int y = graph.get(x).get(i);
if(!visited[y]) dfs(y);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 그래프 초기화
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
// 노드 1에 연결된 노드 정보 저장
graph.get(1).add(2);
graph.get(1).add(3);
graph.get(1).add(8);
// 노드 2에 연결된 노드 정보 저장
graph.get(2).add(1);
graph.get(2).add(7);
// 노드 3에 연결된 노드 정보 저장
graph.get(3).add(1);
graph.get(3).add(4);
graph.get(3).add(5);
// 노드 4에 연결된 노드 정보 저장
graph.get(4).add(3);
graph.get(4).add(5);
// 노드 5에 연결된 노드 정보 저장
graph.get(5).add(3);
graph.get(5).add(4);
// 노드 6에 연결된 노드 정보 저장
graph.get(6).add(7);
// 노드 7에 연결된 노드 정보 저장
graph.get(7).add(2);
graph.get(7).add(6);
graph.get(7).add(8);
// 노드 8에 연결된 노드 정보 저장
graph.get(8).add(1);
graph.get(8).add(7);
dfs(1);
}
}BFS(Breadth First Search)
- BFS는 너비 우선 탐색이라고 부르며, 그래프에서 가까운 노드부터 우선적으로 탐색하는 알고리즘
- BFS는 큐 자료구조를 이용
- 동작과정
- 탐색시작 노드를 큐에 삽입하고 방문처리
- 큐에서 노드를 꺼낸 뒤 해당 노드의 인접 노드중에서 방문하지 않은 노드를 모두 큐에 삽입하고 방문처리
- 더 이상 2번의 과정을 수행할 수 없을 때 까지 반복


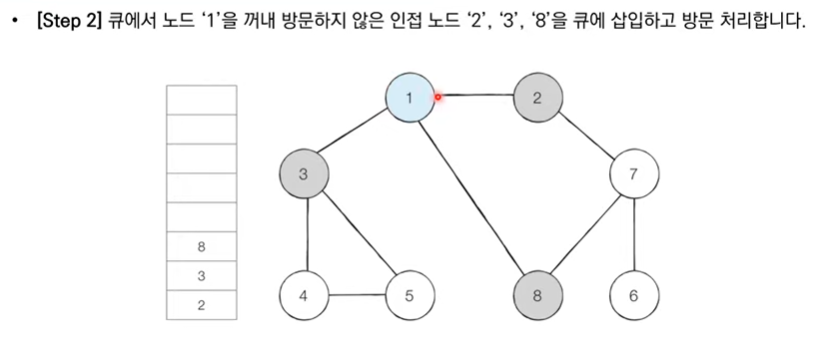
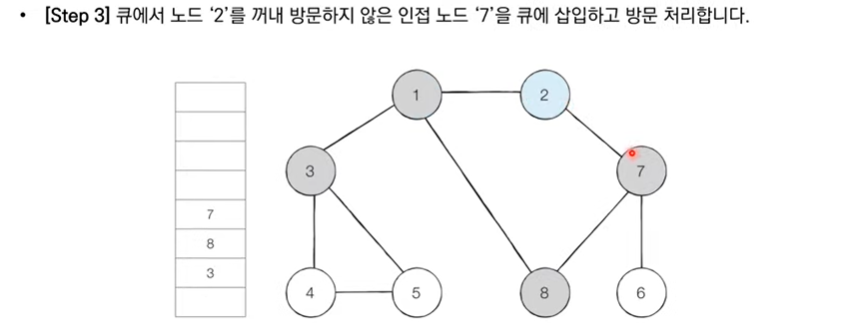

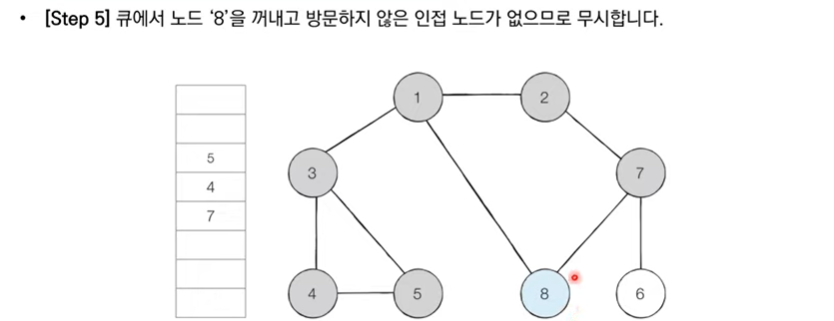

BFS 구현 예제
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static boolean[] visited = new boolean[9];
public static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
// BFS 함수 정의
public static void bfs(int start) {
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(start);
// 현재 노드를 방문 처리
visited[start] = true;
// 큐가 빌 때까지 반복
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
// 큐에서 하나의 원소를 뽑아 출력
int x = q.poll();
System.out.print(x + " ");
// 해당 원소와 연결된, 아직 방문하지 않은 원소들을 큐에 삽입
for(int i = 0; i < graph.get(x).size(); i++) {
int y = graph.get(x).get(i);
if(!visited[y]) {
q.offer(y);
visited[y] = true;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 그래프 초기화
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
// 노드 1에 연결된 노드 정보 저장
graph.get(1).add(2);
graph.get(1).add(3);
graph.get(1).add(8);
// 노드 2에 연결된 노드 정보 저장
graph.get(2).add(1);
graph.get(2).add(7);
// 노드 3에 연결된 노드 정보 저장
graph.get(3).add(1);
graph.get(3).add(4);
graph.get(3).add(5);
// 노드 4에 연결된 노드 정보 저장
graph.get(4).add(3);
graph.get(4).add(5);
// 노드 5에 연결된 노드 정보 저장
graph.get(5).add(3);
graph.get(5).add(4);
// 노드 6에 연결된 노드 정보 저장
graph.get(6).add(7);
// 노드 7에 연결된 노드 정보 저장
graph.get(7).add(2);
graph.get(7).add(6);
graph.get(7).add(8);
// 노드 8에 연결된 노드 정보 저장
graph.get(8).add(1);
graph.get(8).add(7);
bfs(1);
}
}


DFS 해결 코드
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static int n, m;
public static int[][] graph = new int[1000][1000];
// DFS로 특정 노드를 방문하고 연결된 모든 노드들도 방문
public static boolean dfs(int x, int y) {
// 주어진 범위를 벗어나는 경우에는 즉시 종료
if (x <= -1 || x >=n || y <= -1 || y >= m) {
return false;
}
// 현재 노드를 아직 방문하지 않았다면
if (graph[x][y] == 0) {
// 해당 노드 방문 처리
graph[x][y] = 1;
// 상, 하, 좌, 우의 위치들도 모두 재귀적으로 호출
dfs(x - 1, y);
dfs(x, y - 1);
dfs(x + 1, y);
dfs(x, y + 1);
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// N, M을 공백을 기준으로 구분하여 입력 받기
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine(); // 버퍼 지우기
// 2차원 리스트의 맵 정보 입력 받기
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String str = sc.nextLine();
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
graph[i][j] = str.charAt(j) - '0';
}
}
// 모든 노드(위치)에 대하여 음료수 채우기
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
// 현재 위치에서 DFS 수행
if (dfs(i, j)) {
result += 1;
}
}
}
System.out.println(result); // 정답 출력
}
}

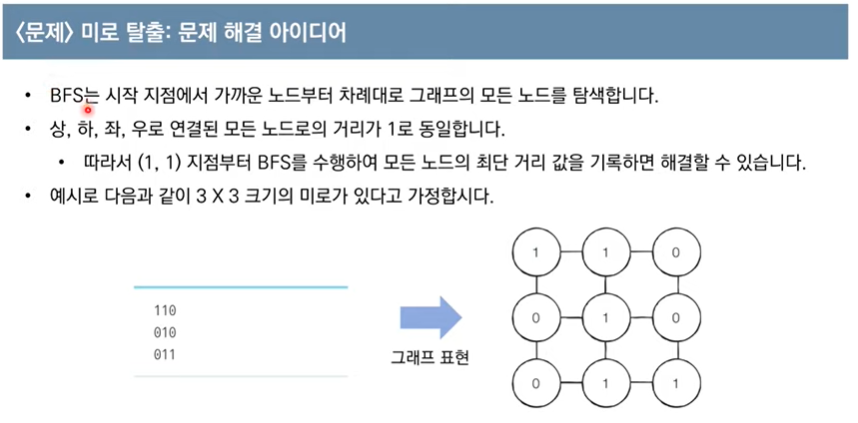
BFS 해결 코드
import java.util.*;
class Node {
private int x;
private int y;
public Node(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public int getX() {
return this.x;
}
public int getY() {
return this.y;
}
}
public class Main {
public static int n, m;
public static int[][] graph = new int[201][201];
// 이동할 네 가지 방향 정의 (상, 하, 좌, 우)
public static int dx[] = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
public static int dy[] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
public static int bfs(int x, int y) {
// 큐(Queue) 구현을 위해 queue 라이브러리 사용
Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(new Node(x, y));
// 큐가 빌 때까지 반복하기
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
Node node = q.poll();
x = node.getX();
y = node.getY();
// 현재 위치에서 4가지 방향으로의 위치 확인
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = x + dx[i];
int ny = y + dy[i];
// 미로 찾기 공간을 벗어난 경우 무시
if (nx < 0 || nx >= n || ny < 0 || ny >= m) continue;
// 벽인 경우 무시
if (graph[nx][ny] == 0) continue;
// 해당 노드를 처음 방문하는 경우에만 최단 거리 기록
if (graph[nx][ny] == 1) {
graph[nx][ny] = graph[x][y] + 1;
q.offer(new Node(nx, ny));
}
}
}
// 가장 오른쪽 아래까지의 최단 거리 반환
return graph[n - 1][m - 1];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// N, M을 공백을 기준으로 구분하여 입력 받기
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine(); // 버퍼 지우기
// 2차원 리스트의 맵 정보 입력 받기
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String str = sc.nextLine();
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
graph[i][j] = str.charAt(j) - '0';
}
}
// BFS를 수행한 결과 출력
System.out.println(bfs(0, 0));
}
}
Reference.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7C9RgOcvkvo&list=PLRx0vPvlEmdAghTr5mXQxGpHjWqSz0dgC&index=3
'알고리즘 > 알고리즘 기초' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 이코테 5. 다이나믹 프로그래밍 (0) | 2023.07.21 |
|---|---|
| 이코테 4. 이진탐색 (0) | 2023.07.20 |
| 이코테 3. 정렬 알고리즘 (0) | 2023.04.29 |
| 이코테 1-1. 구현(Implementation) (0) | 2023.04.15 |
| 이코테 1. 그리디(Greedy) 알고리즘 (0) | 2023.04.15 |




